Pneumonia and bronchitis are notorious for causing a lot of coughing, but does this cough differ between the two conditions?
“It is important to begin by stating the differences between bronchitis and pneumonia,” says Angel Coz, MD, FCCP, board certified pulmonologist, Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Kentucky, Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“Bronchitis is an infection of the airways that typically occurs after an upper respiratory infection such as a cold,” continues Dr. Coz.
“On the other hand, pneumonia is an infection inside the lungs (one or both). Pneumonia can be very dangerous, as it can progress to sepsis which is a life-threatening complication of an infection.
“Sepsis occurs when our own body’s attempt to fight the infection leads to a cascade of events that damage the organs and makes them fail.
“The cough in bronchitis can be productive of green or yellow phlegm, or it could even have blood streaks.
“The cough in pneumonia is also productive of yellow, green or rust colored phlegm that can be thick at times.
“Per se, the characteristics of the cough may not be sufficient to differentiate between bronchitis or pneumonia.
“Pneumonia is associated with other symptoms such as high fevers, chills, shortness of breath, fatigue or lethargy.”
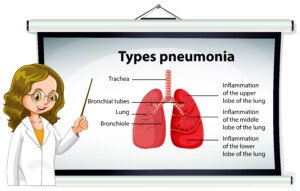
The absence of a fever does NOT rule out pneumonia, as bacteria, rather than a virus, can sometimes be the cause.
“On the other hand, bronchitis can be associated with some chest tightness and is sometimes recognized by patients as a ‘chest cold.’”
Pneumonia Cough vs. Bronchitis: Difference in Sound?
Dr. Coz explains, “The characteristics of the cough are not sufficient to differentiate bronchitis from pneumonia.
“The main difference between pneumonia and bronchitis will be the appearance of other signs of infection in pneumonia that indicate a more severe scenario.”
A Difference in Causes?
“Bronchitis is typically caused by a viral infection that leaves a residual cough that lasts for several weeks and is for the most part not associated with severe symptoms,” explains Dr. Coz.
“On the other hand, pneumonia can be caused by bacteria as well as virus like the flu.
“Bacterial pneumonia should be treated with antibiotics and the flu with antivirals. If left untreated, pneumonia can progress to sepsis and become life threatening.”
Many people who have survived sepsis have lost limbs due to this body-wide infection.
“Signs that pneumonia may have progressed to sepsis include: shivering, generalized pain, discolored skin, sleepiness and shortness of breath.
“If you experience a combination of these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.”
 Dr. Coz is a pulmonary and critical care specialist at the Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center. He has a special interest in sepsis resuscitation and medical education.
Dr. Coz is a pulmonary and critical care specialist at the Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center. He has a special interest in sepsis resuscitation and medical education.
 Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. She’s also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. She’s also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
.