Removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) can cause heartburn due to reflux.
It’s even possible to suffer this heartburn up to four months after gallbladder removal.
For some patients, gallbladder removal is the end of troublesome symptoms – as they are perfectly fine after that.
Other patients, though, have continuing problems, and one of these is acid reflux.
In a study by Jazwari et al, 13 out of 37 people who’d had their gallbladder removed were still experiencing problems as far out as four months.
The 13 patients had had abnormal pH levels in the esophagus before their surgery, but following the cholecystectomy their pH level jumped on average by 73 percent.
How did gallbladder removal cause heartburn in these patients?
The conclusion by the study authors was that there was a compromised sphincter.
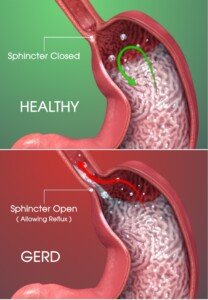
Scientific Animations, CC/BY-SA/Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International
The sphincter is the structure whose job it is to prevent stomach contents (which are acidic) from refluxing up the esophagus.
A weak sphincter will let stomach contents travel up the esophagus. Some causes are as follows:
• Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
• Hiatal hernia
• Obesity or abdominal pressure
• Pregnancy
• Aging-related muscle weakening
• Smoking
• Alcohol
• Certain foods (fatty, acidic, chocolate, caffeine, peppermint)
• Medications (anticholinergics, calcium channel blockers, nitrates, benzodiazepines)
• Diabetes-related nerve damage
• Neurologic disorders (e.g., Parkinson’s disease, stroke)
• Chronic vomiting or retching
This weakening is what causes heartburn, upper abdominal pain, coughing and other symptoms associated with acid reflux.