Ovarian cancer can cause bloating: not just a feeling of bloating, but a visible abdominal distention.
If you have unexplained bloating sensations or your stomach seems to be growing, even though you haven’t been eating more or are not pregnant, make an appointment with your gynecologist, as this could signal fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity.
Though bloating usually is not caused by ovarian cancer, one of this disease’s hallmark symptoms is bloating.
Ovarian cancer is rare, being diagnosed in about 20,000 U.S. women yearly, with 90 percent of them being over age 50.
However, about 70 percent, according to one study, indeed experience bloating as a symptom of their ovarian cancer.
How does ovarian cancer cause bloating?
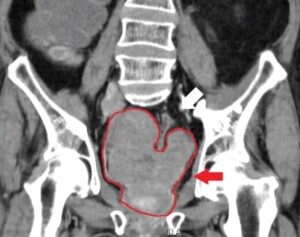
“Advanced ovarian cancer, where the cancer has already spread to other organs, can cause bloating because a liquid, called ascites fluid, is produced,” explains Diane Yamada, MD, Chief, Gynecologic Oncology, University of Chicago Medical Center.
“This may result in a few extra liters of fluid in the abdominal cavity, which can make the patient feel bloated or pregnant.
“Presumably, bloating may also be caused by extensive cancer sitting on the surface of the intestines.”
Ovarian cancer is the deadliest of all gynecological malignancies (killing almost 15,000 U.S. women yearly), because there is no known reliable screening tool.
Even ultrasound is not reliable, as some ovarian tumors can appear benign, while a benign mass, such as a dermoid cyst, can be “viewed as worrisome for cancer,” says Dr. Yamada.
In fact, ultrasound can’t even definitively diagnose a corpus luteum cyst, which is the empty “shell” of an ovarian follicle from which an egg is released every month.
“The quality of ultrasound interpretation also depends on the experience of the ultrasonographer.”
Because of its unreliability, ultrasound has caused many “false positive” results, creating unspeakable anxiety and even unnecessary exploratory surgery for women who turned out to have nothing wrong.
Even the CA 125 blood test is unreliable for detecting this stealthy killer, in that a woman with the disease can have a normal CA 125, and one without the illness can have a high CA 125.
If you are experiencing bloating, don’t jump to the conclusion that it must be ovarian cancer.

Freepik.com
There are many medical conditions that cause bloating, including a benign cyst.
However, if after a few weeks, the bloating does not seem to be resolving, do schedule an appointment with your physician.
Ask your gynecologist if your ovaries are okay.
By the time symptoms of OC start appearing, many times the disease has spread beyond the ovaries, drastically reducing survival rates.
When malignancy is found on one ovary only, some women will elect to have both of the walnut-sized organs removed, while other women will choose to retain the healthy ovary so that they can become pregnant.
However, another option exists:
Harvesting eggs from the healthy ovary, and then having the organ removed.
“This should only be considered after extensive discussion with a cancer specialist, however,” says Dr. Yamada.
Ovarian Cancer Risk Factors
- Postmenopausal age
- Obesity
- Infertility
- Inherited gene mutation
- Family history of the disease
- Breast cancer
Symptoms Other than Bloating
- Digestive disturbances
- Pelvic pain
- Pelvic heaviness
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Feeling full after small meals