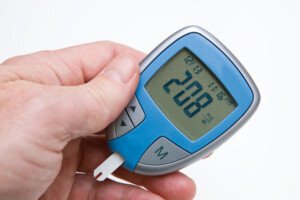
It’s strange that blood sugar in a diabetic can rise despite not having eaten anything, since typically, eating causes blood sugar to go up.
But it’s not an uncommon occurrence that in diabetes, glucose or blood sugar levels can actually rise in the absence of eating.
“When we don’t take food into our body for energy, our liver will try to help us by releasing glucose into our blood so we have the energy we need to stay alive,” says Lucille Hughes, RN, CDE, director of diabetes education at South Nassau Communities Hospital in Oceanside, NY.
“For people with diabetes, the liver may release too much glucose, causing blood sugar to go up.”
This is why it’s so important for diabetics to regularly take blood sugar readings, even if they feel fine.
The liver has hundreds of jobs. One of those jobs is to release glucose into the bloodstream for energy — because the body requires energy to function, even when at rest or asleep.
Basic bodily functions require energy — and glucose provides that energy. Even thinking requires energy.
In diabetes, be it type 1 or type 2, things are out of whack in the body.
The liver in the diabetic individual may sometimes overestimate how much sugar to release into the bloodstream.
Or, to put it another way, the liver may over-correct what it “thinks” is a shortage of blood sugar.
The only way that a diabetic person can stay ahead of this curve is to monitor their glucose levels on a regular basis throughout the day to make sure that the sugar level doesn’t sneak its way into getting into a dangerously high range.
Keeping Blood Sugar Under Control
It’s not enough for those with diabetes to faithfully take glucose readings.
A person with diabetes (either type 1 or type 2), even when they’re not hungry, should not go long periods without eating.
This is because irregular eating patterns can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Skipping meals can cause blood sugar to drop too low, a condition known as hypoglycemia, which can result in symptoms like dizziness, weakness and confusion.
On the other hand, eating in an inconsistent way can also lead to overeating later, potentially causing blood sugar spikes, not to mention weight gain.
Even a snack sized amount of food will help solve the problem of going long periods without eating.
Snack items should include fruit, nuts, seeds, strips of chicken, a few hard boiled eggs, a tuna salad and other foods with limited processing.
 For many years Lucille Hughes has worked as a certified diabetes educator for inpatient acute care, home care, private endocrinology practice and outpatient diabetes education centers.
For many years Lucille Hughes has worked as a certified diabetes educator for inpatient acute care, home care, private endocrinology practice and outpatient diabetes education centers.
 Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. She’s also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. She’s also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
.