Finally, endoscopic surgery for the removal of an acoustic neuroma has arrived, in which the tumor is removed through the ear canal using an endoscope.
The summer of 2016 was a big move ahead for the surgical treatment of acoustic neuroma.
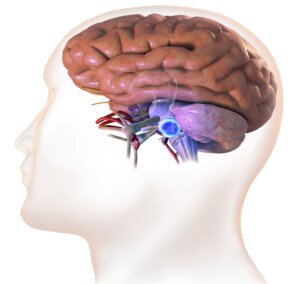
An acoustic neuroma is also known as a vestibular Schwannoma.
It is a very slow growing, benign tumor that is often discovered by accident when the patient receives an MRI for an unrelated issue.
Symptoms of an acoustic neuroma may include:
- Hearing Loss: Often gradual and may affect one ear more than the other.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing in the affected ear.
- Balance Issues: Dizziness or unsteadiness.
- Facial Numbness or Weakness: If the tumor presses on nearby facial nerves.
Traditionally, treatment options have been limited to radiation (which can leave side effects including increasing the risk of cancer) and surgical resection (cutting out the tumor), which in most cases leaves the patient hearing impaired.
Nerve damage from both approaches can result in other residual symptoms such as dizziness, headaches and partial facial numbness and even paralysis.
Wouldn’t it be great if acoustic neuromas could be taken out via the ear canal?
This would eliminate radiation and cutting into the skull.
Two patients in 2016 underwent endoscopy for their acoustic neuromas.
Dr. Brandon Isaacson used an endoscope to reach the tumors and extract them via the inner ear canal.
Dr. Isaacson is associate professor of otolaryngology at UT Southwestern Medical Center.
Though the treatment in some cases for smaller acoustic neuromas involves only surveillance, many other patients must undergo either radiation (radiosurgery) or microsurgery (surgical resection).
The endoscopic option would be available for smaller tumors, which would be removed through the ear canal.
You can easily imagine that if this benign, rare tumor was large, it would not fit through the canal to be removed.
How is endoscopic surgery for acoustic neuroma performed?
• A camera is attached to an endoscope.
• The endoscope consists of a thin metal tube that’s filled with fiberoptic cables.
• The cables transmit images to a TV screen.
• In the ear canal, a small incision is made.
• The endoscope locates the acoustic neuroma and removes it.