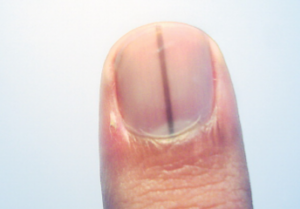
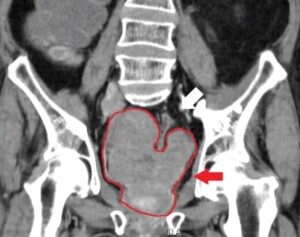
Yes, children, teens and young adults can develop a potentially fatal blood clot, also known as a deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Even fit kids, under the wrong circumstances, can end up with this serious condition that demands immediate treatment.
Blood clots in kids, as well as in adults, pose a serious risk because they can break loose and travel to the lungs, resulting in a potentially life-threatening condition known as a pulmonary embolism.
When a blood clot lodges in the lungs, it obstructs blood flow, which can lead to sudden and severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing and chest pain.
A pulmonary embolism may cause rapid onset of shortness of breath, sharp or stabbing chest pain, and in some cases, even coughing up blood.
Immediate medical attention is crucial for managing a pulmonary embolism, as prompt treatment can significantly impact the outcome and reduce the risk of severe complications or death.
Young adults and children are not immune to DVT , which is a blood clot in a vein.
DVT stands for deep vein thrombosis. It’s a clump of blood — a sticky thick network of blood cells — attached to the inner wall of a vein, obstructing blood flow.
“Kids and teens are treated for blood clots according by identifying the underlying cause of the blood clot,” says Dr. Lisa Lewis, MD, a board certified pediatrician in Fort Worth, Texas, and author of “Feed the Baby Hummus, Pediatrician-Backed Secrets from Cultures Around the World.”
“Typically, blood clots are treated with an anticoagulant [blood thinner] and sometimes aspirin.”
Blood thinners would include heparin, or its low molecular weight version, given with warfarin (Coumadin), or just warfarin alone.
The INR blood work is taken on a scheduled basis so that the effect of the anticoagulant drug can be monitored to ensure it stays within therapeutic range.
“Although uncommon, a large percentage of blood clots in children and teens are inherited,” says Dr. Lewis.
What if a child or young adult has an acute, large DVT?
A large deep vein thrombosis can completely obstruct flow of blood from a limb.
In this case, other medications may be used early on, such as a thrombolytic (clot-busting) agent. This would be followed by anticoagulant medications.
Long-term management of deep vein thrombosis (and pulmonary embolism) in kids:
1) The safe prevention of additional DVTs is emphasized
2) Management is designed to enable the young patient to function as normally as possible.